PITTSBURGH—Disney Researchers are harvesting vitality from ambient radio waves generated by TV, radio and cellphones to energy the networks that assist the so-called “Internet of Things,” or IoT.
“This is achieved via ultra-wideband backscatter methods that leverage the breath of business broadcast indicators within the 80 MHz to 900 MHz vary from FM radios, digital TVs, and mobile networks,” a trio of Disney researchers mentioned in a paper entitled, “Riding the Airways: Ultra-Wideband Ambient Backscatter via Commercial Broadcast Systems.”
According to Disney, researchers led by Alanson Sample, affiliate lab director and chief of the Disney Research Wireless Systems group, created an “ultra-low-power system of sensors that transmit information to a central receiver by reflecting the ambient radio waves from business broadcasting methods that already bathe most workplace environments.”
The system is enabled by means of common backscatter readers that energy “a community of ultra-low energy nodes to function on ambient carriers as little as -80 dBm, which is typical for indoor residence and workplace environments. For the primary time, we reveal the simultaneous use of 17 ambient sign sources to attain node-to-reader communication distances of 50 meters, with information charges as much as 1 kbps,” the paper states.
Simply put, Sample mentioned, “Our thought is to reuse all of the radio indicators which might be round us as a medium for transmitting information, very like sending ripples throughout a pond.”
The strategy is claimed to “radically” scale back energy necessities for the sensor nodes as a result of producing radio waves is what consumes most of their battery energy. The researchers stuffed the remaining “tiny little bit of energy demand” of their experiment “utilizing photo voltaic cells optimized for low-light circumstances.”
Sample, together with Disney’s Chouchang Yang and Jeremy Gummeson, introduced particulars of system at the IEEE Conference on Computer Communication, INFOCOM 2017, in Atlanta, Ga. Disney mentioned the group “demonstrated the system in an indoor workplace setting, utilizing ambient indicators from 14 radio towers in addition to two cellphones. ”
“The promise of the Internet of Things is that wi-fi sensors might be ubiquitous, permitting units to sense their environments and speak to one another,”mentioned Markus Gross, vice chairman at Disney Research. “As we transfer in direction of connecting the following billion wi-fi units to the web, nonetheless, the usage of batteries to energy these units will turn into unworkable. UWB ambient backscatter methods, which doubtlessly may very well be deployed in any metropolitan space, maintain nice potential for fixing this dilemma.”
Backscatter communication is now employed in in passive RFID tags, however the restricted vary makes it “impractical for IoT methods,” Disney mentioned. The similar was true of utilizing a single supply for ambient RF, resembling a TV station.
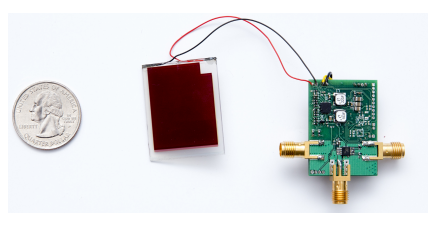 |
| Image of the ultra-wideband ambient backscatter node with photo voltaic cell for vitality autonomous sensing and computing. |
Sample mentioned the multiple-source strategy boosted the signal-to-noise ratio, “considerably enhancing the sensitivity of the backscatter reader and lowering useless zones.” This was mentioned to allow the system to function on “real-world ambient sources” at a variety of as much as 22 meters on broadcast sources and as much as 50 meters on mobile uplink site visitors.
Sample additionally mentioned the ultra-low-power sensor nodes are easy, and that the backscatter readers do “the heavy lifting” by decoding and mixing a number of backscatter carriers to get well information from every sensor utilizing 4 software-defined receivers—one every for FM and mobile and two for digital TV. Since the isn’t tuned to particular frequencies, it may be deployed in“virtually any metropolitan space,” he mentioned.